Software development Methodology analysis – Waterfall versus Agile
Focal Points
- Standard or Waterfall approach
- Agile Methodology
- Differences between Waterfall and Agile
- Indicators to select the correct methodology
- Methodology Selection
- Common terminologies
Standard or Waterfall approach
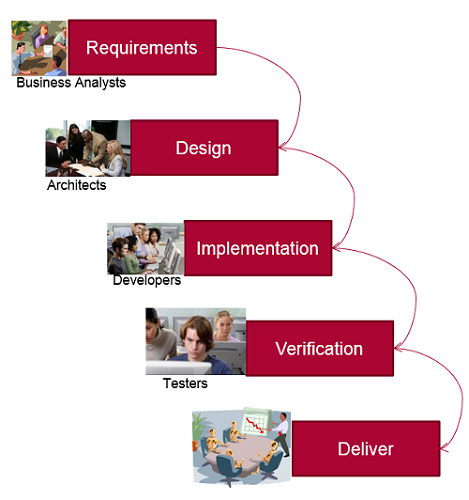
- Sequential development model
- Moves to next phase only when the current phase is complete
- Clear, fixed and approved requirements
- Scope changes are handled by Change control process.
- Specific skill set required per phase
- Requirements - Business analysts
- Design - Architects
- Implementation - Developers
- Verification - Testers
- Easy to plan
Waterfall - Pros & Cons
|
Pros |
|
Cons |
|
|
Agile Methodology
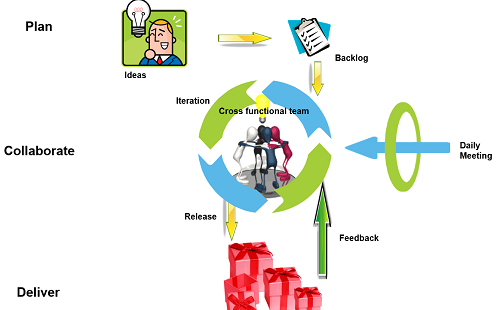
Agile Methodology has three repetitive phases
Plan
- The business partner or customer lists down his requirements for the project.
- The requirements are shuffled as per priority.
- Few requirements are selected based on feasibility and priority for iteration in collaborate phase
Collaborate
- Cross functional team
- Team includes business analyst, developer, tester and manager
- Requirements selected for the iteration are taken and the standard software development phases, "requirements - design - development - testing" are carried out.
- Agile methodology also includes a daily meeting to discuss and identify the show stoppers, pitfalls and solutions.
Deliver
- Deliverable or Output of the iteration is shared with the business partner or customer.
- Feedback if any from the partner is shared with the team.
- Team scribes those feedback in the backlog list.
Now again the process starts from step 1, that is, prioritizing and identifying requirements for next iteration.
The cycle goes on and on till all the requirements are met.
Key features of Agile
- 4 Principles:
- Individuals & interactions over processes & tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over plan follow-throughs
- Very flexible approach
- Accepts that Business requirements will change over the course of time
- Does not expect every requirement to be known before starting
- Requires business partner involvement throughout the entire process
- Breaks project down into small “iterations”
Agile - Pros & Cons
|
Pros |
|
Cons |
|
|
Differences between Waterfall and Agile

|
Waterfall |
|
Agile |
|
Predictable approach |
Adaptable approach |
|
|
Plan driven approach |
Value driven approach |
|
|
Sequential process |
Continuous Process |
|
|
Set of different teams work separately |
Single cross functional team |
|
|
Less business partner involvement |
High business partner involvement |
|
|
Difficult to make changes |
Easy to change with each sprint |
|
|
Detailed signed off requirements |
Incomplete Requirements |
Indicators to select the correct methodology
|
Criteria |
|
Yes? |
|
No? |
|
Clear and fixed requirements |
Waterfall |
Agile |
||
|
High business partner involvement |
Agile |
Waterfall |
||
|
Detailed documentation approach? |
Waterfall |
Agile |
||
|
End timeline constraint? |
Waterfall |
Agile |
||
|
Very high level control & reporting? |
Waterfall |
Agile |
||
|
Expect changes in the later project phases? |
Agile |
Waterfall |
||
|
Scope changes? |
Agile |
Waterfall |
Methodology Selection
In this section let us walk through couple of commonly used methods to make the correct methodology choice.
Method 1 - Average score method
Fill in the score in the below table based on your project criteria
|
# |
|
Criteria |
|
Score (0 – Less likely ; 100 – More likely) |
|
1 |
Incremental project delivery |
|||
|
2 |
Dedicated core team |
|||
|
3 |
Adaptive planning and quick escalations |
|||
|
4 |
High commitment & availability of business partners |
|||
|
5 |
Easy to automate the test environment |
|||
|
6 |
Unclear requirements and more chances of scope creep |
|||
|
7 |
A small cross functional team is sufficient |
|||
|
8 |
Project focused on a single system but with many interfaces |
|||
|
9 |
Continuous integration is possible |
|||
|
10 |
Minimal dependency on other projects |
|||
|
Average Score |
If Average score,
is greater than 55 – Suitable for Agile approach
falls between 25 and 55 – Suitable for Hybrid approach (mixture of Agile and Waterfall)
less than 25 – Suitable for Standard approach
Method 2 - Radar method
Enter the value in the below table based on your project criteria.
|
# |
Criteria |
Value |
||
|
1 |
Team size (in number) |
|||
|
2 |
|
Criticality: Select one
|
|
|
|
3 |
Requirement changes (% changes per month) |
|||
|
4 |
Availability of experienced resources (in number) |
|||
|
5 |
Less orderly environment (in %) |
Use the values to plot the graph as shown below:
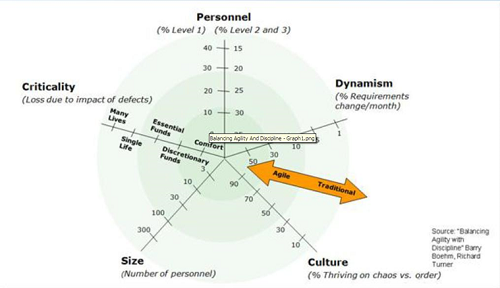
The closer the plotted points are to the center, Agile is the better choice. Else Waterfall is the choice.
Common Terminologies
|
# |
Term |
Definition |
||
|
1 |
|
Sprint |
|
An iterative unit of time. Sprints allow teams to leverage incremental improvements. |
|
2 |
Scope Creep |
The uncontrolled growth of the project scope resulting from constant changes to requirements without consideration to the impact on resources or timescale. |
||
|
3 |
Scope |
The overall definition of what the project should achieve and a specific description of what the result should be. |
||
|
4 |
Deliverable |
A tangible or intangible object produced through project execution. A deliverable can be created from multiple smaller deliverables. |
||
|
5 |
Change Control |
The practice of identifying, documenting, approving and carrying out changes within a project. |
||
|
6 |
Time-box |
A time-box is a previously agreed period of time during which a team works steadily towards completion of some goal. Rather than allow work to continue until the goal is reached, and evaluating the time taken, the time-box approach consists of stopping work when the time limit is reached and evaluating what was accomplished. |